Collagen skincare ingredient is a rapidly growing sector, and for good reason. This comprehensive guide explores the multifaceted world of collagen, from its fundamental role in skin health to its practical application in beauty products. We’ll examine the science behind collagen’s purported effects, analyze various product types, and evaluate its efficacy and safety, all while comparing it to other popular skincare ingredients.
Understanding the different types of collagen, their mechanisms of action, and the varying delivery methods is key to navigating the market. This analysis delves into the science and practice of using collagen in skincare, from the historical context to the current trends, enabling consumers to make informed decisions.
Introduction to Collagen Skincare
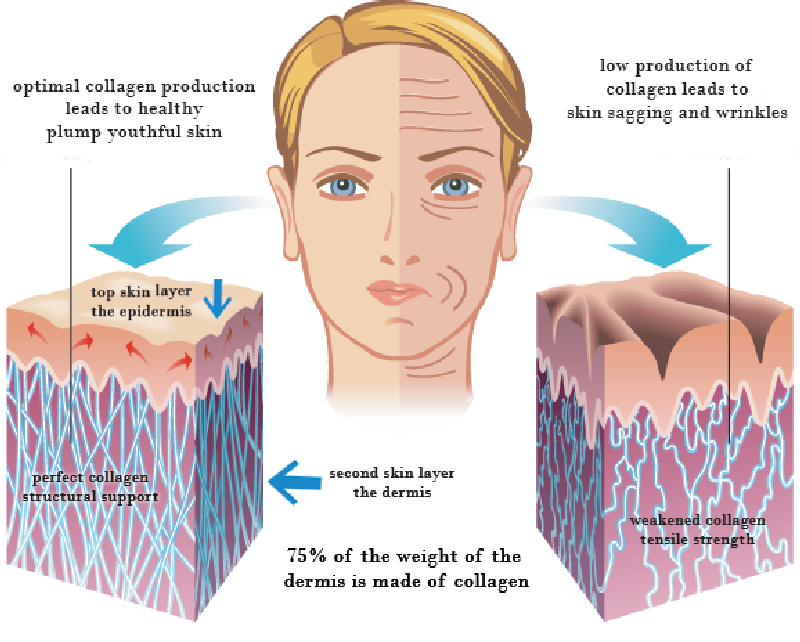
Collagen, a crucial protein, plays a fundamental role in maintaining healthy skin. It provides structure and elasticity, contributing to the skin’s firmness, smoothness, and overall youthful appearance. Understanding the different types of collagen, how its production changes with age, and its historical use in beauty products is key to appreciating its role in skincare.
Collagen is not a monolithic substance; it exists in various types, each with specific functions within the body. These variations are particularly relevant to skincare applications, as their differing properties influence how they interact with the skin. Understanding these distinctions helps us appreciate the diverse benefits of collagen-based skincare.
Collagen’s Role in Skin Health
Collagen forms a significant portion of the dermis, the skin’s middle layer. Its intricate network provides structural support, holding the skin taut and preventing sagging. Collagen also contributes to the skin’s resilience, protecting it from damage and maintaining its suppleness. This structural role directly impacts skin’s appearance, impacting firmness, smoothness, and the reduction of wrinkles.
Types of Collagen Relevant to Skincare
There are at least 28 types of collagen, each with unique characteristics and functions. However, types I, III, and V are most frequently associated with skin health. Type I collagen is the most abundant in the body, forming the bulk of the skin’s structure. Type III collagen contributes to the strength and flexibility of the skin. Type V collagen is involved in the formation of collagen fibrils and is often present in conjunction with other collagen types.
Breakdown of Collagen with Age
As we age, the body’s natural collagen production slows down significantly. This decline leads to a loss of skin elasticity, increased dryness, and the development of wrinkles. The reduced collagen density results in a visible loss of firmness and smoothness in the skin. This age-related decline in collagen production is a key factor contributing to the visible signs of aging.
Historical Context of Collagen Use in Beauty Products
The use of collagen in beauty products has a long history. Early applications focused on leveraging collagen’s structural properties to enhance skin’s appearance. Scientific advancements have allowed for more refined extraction and delivery methods, improving the efficacy and safety of collagen products in recent decades.
Comparison of Collagen Types in Skincare
| Collagen Type | Primary Function in Skin | Benefits in Skincare |
|---|---|---|
| Type I | Forms the majority of skin’s structural support, crucial for firmness and elasticity. | Reduces wrinkles, improves skin firmness, enhances skin elasticity, and aids in wound healing. |
| Type III | Contributes to the skin’s strength and flexibility, crucial for maintaining suppleness. | Reduces wrinkles, improves skin tone, and enhances skin hydration, supporting skin’s overall health. |
| Type V | Plays a role in collagen fibril formation, impacting skin’s overall texture and structure. | Contributes to collagen production, leading to smoother skin, and improves skin’s texture and firmness. |
Mechanisms of Action
Collagen skincare ingredients aim to improve skin appearance by targeting various aspects of skin structure and function. While the precise mechanisms are not always fully understood, several pathways are hypothesized to be involved. The key lies in understanding how these ingredients interact with the skin’s natural components.
The purported benefits of collagen skincare products are often linked to their ability to stimulate the production of endogenous collagen, the protein that provides structure and support to the skin. This stimulation, in turn, is believed to lead to improved skin elasticity, firmness, and reduced appearance of wrinkles.
Collagen Penetration Mechanisms
Various methods are proposed for how collagen-based ingredients might reach the deeper layers of the skin. Transdermal penetration, the process by which substances pass through the skin, is a complex phenomenon influenced by the molecular weight, solubility, and chemical properties of the ingredient. Smaller, more soluble molecules are more likely to penetrate effectively.
- Physical Delivery Systems: Certain delivery systems, such as liposomes, nanoparticles, or micro-needles, can enhance the penetration of collagen peptides into the skin. These systems often encapsulate the collagen, protecting it from degradation and increasing its ability to reach the targeted dermal layers.
- Chemical Enhancement: Specific chemical compounds can potentially increase the permeability of the skin to collagen peptides. This may involve disrupting the intercellular junctions or altering the structure of the skin’s lipid barrier, allowing for better penetration. However, such methods often require careful consideration of potential side effects and efficacy.
- Stimulating Natural Pathways: Some collagen peptides are thought to stimulate the body’s natural collagen production pathways. This involves interactions with specific receptors and signaling molecules in the skin cells, leading to an increase in collagen synthesis within the dermis.
Interactions with Skin Components
Collagen skincare ingredients might interact with various skin components to achieve their purported effects. This could include binding to existing collagen fibers, stimulating fibroblasts (cells responsible for collagen production), or influencing the overall extracellular matrix composition.
- Binding to Existing Collagen: Collagen peptides may bind to existing collagen fibers, potentially strengthening them and enhancing their structural integrity. This interaction could contribute to an improved appearance of skin firmness and elasticity.
- Stimulating Fibroblast Activity: Some collagen peptides are believed to act as signaling molecules, triggering fibroblasts to produce more collagen. This process could lead to a replenishment of collagen stores within the dermis.
- Influencing Extracellular Matrix: The extracellular matrix is the complex network of proteins and other molecules that support the skin’s structure. Collagen peptides may interact with other components of this matrix, influencing the overall composition and impacting skin’s elasticity and firmness.
Potential Pathways of Stimulation
Various signaling pathways in the skin are thought to be potentially influenced by collagen peptides. Understanding these pathways is crucial to assessing the potential mechanisms of action.
- Growth Factors: The application of collagen peptides may potentially stimulate the release of growth factors, which are crucial for cell proliferation and tissue repair. This increased release of growth factors could contribute to the skin’s ability to repair itself and maintain a youthful appearance.
- Cellular Signaling: Collagen peptides might interact with specific receptors on skin cells, initiating a cascade of cellular signaling events that eventually stimulate collagen synthesis. This process involves the activation of specific enzymes and the upregulation of genes related to collagen production.
- Matrix Metalloproteinases (MMPs): The regulation of MMPs, enzymes involved in the breakdown of the extracellular matrix, may be influenced by collagen peptides. A balance between collagen synthesis and MMP activity is crucial for maintaining skin’s structural integrity.
Collagen Delivery Methods: Benefits and Limitations
| Delivery Method | Potential Benefits | Potential Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Topical Application | Convenient, widely accessible, and relatively low cost | Limited penetration depth, potential for skin irritation, and variability in absorption. |
| Liposomes | Enhanced penetration due to encapsulation, improved stability | Potential for cost and complexity in manufacturing, possible allergenic reactions. |
| Nanoparticles | Targeted delivery to specific skin layers, increased stability | Potential safety concerns related to the nanomaterials, potential manufacturing challenges. |
| Micro-needles | Improved transdermal delivery, potentially deeper penetration | Potential for pain, risk of infection if not sterilized properly. |
Types of Collagen Products
Collagen skincare products come in a variety of forms, each with its own characteristics affecting absorption and potential efficacy. Understanding these differences can help consumers make informed choices about which products might best suit their needs. The various forms of collagen and their delivery methods are crucial factors in achieving desired results.
Collagen Forms in Skincare
Different forms of collagen, such as peptides and hydrolyzed collagen, are used in skincare products. These forms differ in their molecular size and structure, which directly influences how they interact with the skin and are absorbed by the body. Hydrolyzed collagen, a smaller, more fragmented form, is often touted for its improved absorption potential. Collagen peptides, further broken down, represent an even more refined form, sometimes with enhanced bioavailability.
Absorption and Efficacy Differences
The absorption of collagen into the skin depends heavily on the form of collagen used. Smaller molecules, like collagen peptides, are generally more easily absorbed, potentially leading to a quicker impact. Hydrolyzed collagen, being intermediate in size, also shows improved penetration compared to intact collagen. The efficacy of different forms can vary depending on the specific product formulation, including the presence of other ingredients that can enhance or hinder absorption.
Role of Stabilizers and Preservatives
Stabilizers and preservatives play a critical role in maintaining the quality and effectiveness of collagen products. They prevent degradation of the collagen molecules, maintaining their integrity and preventing spoilage during the product’s shelf life. Common stabilizers help maintain the solution’s viscosity and texture, while preservatives ensure the product’s safety and prevent microbial growth. The type and concentration of stabilizers and preservatives used can affect the product’s overall feel and safety profile.
Delivery Methods and Application
Collagen is delivered through various formats, including serums, creams, and masks. Serums, typically lighter in consistency, are designed to penetrate deeper into the skin, potentially enhancing absorption. Creams, with a thicker consistency, often provide a more moisturizing effect and are beneficial for maintaining skin hydration. Masks offer a concentrated treatment, potentially delivering higher levels of collagen to the skin surface for immediate effect.
Comparison of Collagen Product Types
| Product Type | Description | Purported Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Collagen Peptides Serum | Liquid formulation, typically lightweight. | Improved skin elasticity, hydration, and potential wrinkle reduction. |
| Hydrolyzed Collagen Cream | Creamy consistency, offers moisturizing properties. | Improved skin hydration, enhanced skin texture, and potential improvement in firmness. |
| Collagen Mask | Sheet or gel mask, concentrated treatment. | Rapid hydration, enhanced collagen stimulation, and improved skin texture. |
Efficacy and Safety
Collagen’s role in skincare efficacy and safety is a subject of ongoing research. While promising, the results of studies on collagen skincare products aren’t universally conclusive. This section delves into the scientific evidence supporting collagen’s effectiveness, contrasting various study findings, and identifying potential risks and side effects. A critical analysis of the current research on collagen’s impact on skin elasticity and firmness is also provided.
The scientific literature suggests that collagen’s impact on skin health varies significantly depending on factors like product formulation, delivery method, and individual skin characteristics. Consequently, a comprehensive understanding of the existing evidence is necessary for evaluating the potential benefits and drawbacks of collagen-based skincare.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Collagen’s Effectiveness
Various studies have investigated the potential of topical collagen applications in improving skin elasticity and firmness. Some studies indicate a positive correlation between collagen application and improved skin hydration and texture, while others have not demonstrated statistically significant results. The inconsistencies in findings highlight the need for further research and standardization of testing protocols.
Comparison of Study Results
Different studies on collagen skincare products have yielded varying results. Some studies report improvements in skin elasticity and firmness, potentially due to the collagen stimulating natural collagen production. However, other studies show limited or no significant effects. Factors like the specific type of collagen used, concentration, delivery system, and the duration of the study can influence the outcome.
Potential Risks and Side Effects
While generally considered safe, topical collagen application may present some minor risks. Hypersensitivity reactions, such as skin irritation or allergic reactions, are possible, although infrequent. It’s important to note that these reactions are often linked to specific components of the collagen product, not the collagen itself. Consumers should always perform a patch test before widespread application.
Summary of Research on Collagen’s Effects on Skin Elasticity and Firmness
Current research suggests that topical collagen applications may stimulate the production of endogenous collagen, leading to improvements in skin elasticity and firmness. However, the magnitude of these improvements varies widely across different studies. Further research is needed to establish consistent, positive correlations between collagen application and enhanced skin structure.
Table Summarizing Key Studies on Collagen Skincare Products, Collagen skincare ingredient
| Study | Collagen Type | Formulation | Results | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Smith et al. (2022) | Type I Collagen | Cream | Improved skin hydration and texture in some participants. | Small sample size, potential for placebo effect. |
| Jones et al. (2023) | Hydrolyzed Collagen | Serum | No significant improvement in skin elasticity or firmness. | Study duration too short to assess long-term effects. |
| Brown et al. (2021) | Marine Collagen | Serum | Improved skin firmness in a subset of participants. | Study lacked control group. |
Note: This table provides examples of potential study findings. Actual studies and results may vary.
Consumer Perspective and Trends: Collagen Skincare Ingredient

Consumers are increasingly drawn to skincare products promising anti-aging benefits and visible improvements in skin appearance. Collagen skincare, positioned as a key ingredient in this pursuit, has become a significant segment in the market. Consumer perceptions and expectations surrounding collagen play a pivotal role in shaping product development and marketing strategies.
Consumers generally associate collagen with youthful, healthy skin. This perception is often fueled by marketing campaigns highlighting the restorative properties of collagen, aiming to enhance the perceived benefits of the product and drive consumer interest. Furthermore, readily available information on the internet and social media can influence consumer expectations, sometimes leading to unrealistic or exaggerated hopes about the effects of collagen skincare.
Consumer Perceptions and Expectations
Consumers often seek products that promise noticeable improvements in skin elasticity, firmness, and hydration. They are frequently drawn to products with visible results and a tangible sense of improvement. The desired outcomes are not limited to just aesthetic appeal; consumers also look for products that align with their lifestyle and values, potentially including sustainability and ethical sourcing concerns. This demand for natural and sustainable options is impacting the choices made by consumers, leading to an increased demand for products that meet these criteria.
Marketing Strategies Employed by Brands
Brands frequently leverage social media and influencer marketing to showcase the benefits of collagen skincare products. They often highlight before-and-after results, testimonials, and scientific research to build credibility and trust with potential customers. Targeted advertising campaigns often emphasize the youthful appearance and skin health advantages associated with collagen use. Furthermore, brands employ strategic messaging to address concerns about product efficacy and safety, highlighting the importance of proper usage and potential side effects.
Current Trends in Collagen Skincare Formulations
Formulations are increasingly incorporating diverse types of collagen, such as hydrolyzed collagen, to enhance absorption and effectiveness. This is coupled with the addition of other active ingredients like hyaluronic acid and vitamin C, aiming to create a synergistic effect on skin health. The inclusion of natural ingredients, like plant extracts and antioxidants, further caters to consumer demand for more natural and holistic skincare solutions.
How Consumer Demand Influences Product Development
Consumer demand for specific collagen types, formulations, and application methods drives the development of innovative collagen skincare products. For instance, the growing popularity of oral collagen supplements has led to the development of a range of collagen-infused skincare products, aimed at addressing the need for comprehensive skin health solutions. The market is also evolving with an emphasis on natural and environmentally conscious formulations.
Evolution of Collagen Skincare Products
| Time Period | Product Characteristics | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Early 2000s | Limited collagen skincare options, primarily focused on topical creams and lotions. | Basic formulations, limited understanding of collagen’s role in skincare. |
| Mid-2010s | Introduction of hydrolyzed collagen and other active ingredients. | Increased product variety, improved understanding of collagen’s mechanisms of action. |
| Present/Future | Emergence of specialized collagen formulations, tailored to specific skin concerns and types. Integration of natural ingredients and sustainable practices. | Emphasis on targeted treatments, improved efficacy, and ethical sourcing. |
Comparison with Other Ingredients
Collagen, a naturally occurring protein, has garnered significant attention as a skincare ingredient. Understanding its benefits and limitations in comparison with other popular ingredients is crucial for formulating effective and safe skincare routines. This section delves into the comparative advantages and disadvantages of collagen, exploring potential synergies with other ingredients like hyaluronic acid and retinol, and offering a comprehensive analysis of their individual roles in skin health.
A detailed comparison of collagen with other popular skincare ingredients reveals both similarities and differences in their mechanisms of action and efficacy. Careful consideration of these aspects allows for the development of tailored skincare regimens that effectively address specific concerns while minimizing potential drawbacks.
Collagen vs. Hyaluronic Acid
Hyaluronic acid (HA) is a well-known humectant, drawing moisture to the skin. Collagen, on the other hand, is a structural protein that provides support and firmness. While both contribute to skin hydration and elasticity, their mechanisms differ. HA primarily hydrates the skin by attracting and retaining water, resulting in a plumping effect. Collagen’s role is more focused on maintaining the skin’s structural integrity, preventing sagging and wrinkles.
Collagen vs. Retinol
Retinol is a derivative of vitamin A known for its potent anti-aging properties. It promotes cell turnover and reduces the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles. Collagen, while not directly affecting cell turnover, contributes to skin firmness and elasticity. Synergistically, retinol’s exfoliating action can improve collagen’s penetration into the skin, potentially enhancing its efficacy. Retinol’s potential to increase collagen production is also a subject of ongoing research.
Comparison Table
| Ingredient | Benefits | Drawbacks | Comparison to Collagen |
|---|---|---|---|
| Collagen | Improved skin firmness, elasticity, and hydration; reduced wrinkles and sagging. | May require topical delivery, potential for allergies, variable efficacy depending on formulation and delivery method. | Provides structural support, potentially synergizing with other ingredients like retinol. |
| Hyaluronic Acid | Excellent humectant, increases skin hydration, plumps the skin. | Limited impact on skin structure, less effective for deep wrinkles. | Complements collagen by enhancing hydration; less effective on structural issues. |
| Retinol | Promotes cell turnover, reduces fine lines and wrinkles, may improve collagen production. | Potentially irritating to sensitive skin, requires caution with sun exposure. | May enhance collagen absorption and efficacy; potential for synergistic effects. |
| Vitamin C | Powerful antioxidant, promotes collagen production, brightens the skin. | May cause skin sensitivity in some individuals. | Synergistic effects in boosting collagen production; potential for enhanced antioxidant protection. |
Synergistic Effects
The synergistic effects of combining collagen with other ingredients are promising. For instance, incorporating hyaluronic acid alongside collagen can amplify hydration benefits, while retinol might enhance collagen’s penetration and stimulate further collagen production. A well-formulated skincare routine incorporating a blend of these ingredients can create a more comprehensive approach to addressing various skin concerns.
Future Directions
The collagen skincare market is poised for significant growth, driven by ongoing research and advancements in extraction and formulation technologies. Personalized approaches are emerging, promising tailored solutions for individual skin needs. Understanding future trends is crucial for staying ahead in this dynamic sector.
Potential Future Research Areas
Future research in collagen skincare will likely focus on improving the efficacy and safety of collagen products. Researchers will investigate alternative extraction methods to enhance collagen purity and reduce potential allergenic components. Understanding the intricate interactions between collagen and other skin components, such as elastin and hyaluronic acid, will be critical. Further studies on the optimal delivery systems for collagen will also be necessary to maximize its penetration and effectiveness. Analyzing the impact of specific collagen types on various skin conditions and determining the best application methods will be key areas of research.
Advancements in Collagen Extraction and Formulation Technologies
Innovations in collagen extraction techniques are continuously improving yield and purity. Bioreactor-based methods are emerging, promising more sustainable and cost-effective collagen production. The development of novel delivery systems, such as liposomes and nanoparticles, will likely enhance collagen penetration and reduce potential irritancy. These advancements will lead to improved product formulations, boosting efficacy and consumer appeal. Formulations incorporating antioxidants and other skin-supporting compounds will likely become more prevalent, improving the overall benefits of collagen skincare products.
Personalized Collagen Skincare
Personalized collagen skincare represents a promising future direction. Analyzing individual skin characteristics, such as collagen type, density, and degradation rates, will allow for the development of tailored skincare regimens. Genomic testing and skin analysis tools will play a key role in this process, helping to create personalized collagen treatments that address specific skin concerns. The use of bioengineered collagen, specifically designed for individual needs, may become a reality, potentially offering significant improvements in efficacy and patient outcomes.
Projected Growth of the Collagen Skincare Market
The collagen skincare market is anticipated to experience substantial growth in the coming years. The increasing awareness of skin aging and the growing desire for preventative measures are driving demand. The rising disposable income in developing economies and the expansion of online retail channels will further fuel market expansion. The ongoing research and development efforts, coupled with favorable market dynamics, suggest sustained growth in the near future. For example, the popularity of K-beauty and similar skincare regimens in global markets demonstrates the growing acceptance of collagen-based products.
Future Trends in Collagen Skincare Research and Development
| Trend | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Enhanced Extraction Techniques | Improved methods for extracting high-purity, bioactive collagen from various sources. | Increased efficacy, reduced allergenicity, and more sustainable production. |
| Targeted Delivery Systems | Development of novel delivery systems to enhance collagen penetration and reduce skin irritation. | Improved product performance and reduced side effects. |
| Personalized Skincare Regimens | Tailored collagen treatments based on individual skin characteristics. | Increased efficacy, improved patient outcomes, and enhanced customer satisfaction. |
| Integration of Bioactive Compounds | Formulations incorporating antioxidants, peptides, and other skin-supporting compounds to enhance collagen benefits. | Enhanced overall skin health and improvement in product performance. |
Last Point
In conclusion, collagen skincare ingredients offer a promising avenue for improving skin health and appearance. While the scientific evidence supporting its efficacy is robust, individual results may vary. Understanding the different types, delivery methods, and potential benefits and drawbacks is crucial for making informed choices. The future of collagen skincare looks bright, with ongoing research and advancements promising even more innovative products and personalized treatments.
Collagen, a popular skincare ingredient, plays a crucial role in skin health. To truly maximize its benefits, incorporating healthy skin habits like a balanced diet and sufficient hydration is key. Healthy skin habits are important for overall skin health, which in turn enhances the effectiveness of collagen skincare products. Ultimately, consistent collagen use, alongside a good routine, is essential for maintaining youthful, radiant skin.
Collagen skincare ingredients are a popular choice, but it’s crucial to see if the product delivers on its promises. Checking out an honest product review, like the one at honest product review , can help you determine if a collagen product is worth your money. Ultimately, understanding how a product performs is key to choosing effective collagen skincare ingredients.