Sun protection tips sets the stage for a crucial discussion on safeguarding your skin from the harmful effects of the sun. Understanding UV radiation, SPF values, and appropriate sunscreens is essential for maintaining healthy skin, regardless of your skin type or activity level.
This comprehensive guide explores various aspects of sun protection, from choosing the right clothing and hats to applying sunscreen effectively. It also delves into specific needs for different individuals, including children, the elderly, and those with specific skin conditions. Furthermore, we’ll discuss how to adapt sun protection strategies for diverse environments and daily routines.
Sun Protection Basics
Protecting your skin from the sun is crucial for maintaining its health and preventing long-term damage. Regardless of skin tone, everyone is susceptible to sun damage, and consistent sun protection is essential for overall well-being. Understanding the different types of UV radiation and how SPF works can empower you to make informed choices for optimal sun safety.
Protecting your skin from the sun’s harmful rays is vital, especially as prolonged exposure can lead to premature aging, sunburn, and an increased risk of skin cancer. Different skin types have varying sensitivities to UV radiation, necessitating tailored sun protection strategies. A comprehensive understanding of UV radiation, SPF, and appropriate sun protection measures will equip you with the knowledge to safeguard your skin effectively.
Importance of Sun Protection for Different Skin Types
All skin types need protection from the sun’s harmful UV rays. While darker skin tones naturally have higher melanin levels, offering some inherent protection, they are still susceptible to sun damage. The severity of damage may vary, but consistent sun protection remains crucial for all skin types to prevent long-term effects like premature aging and skin cancer. It’s important to remember that sun damage can accumulate over time, regardless of current skin tone or perceived sensitivity.
Types of Ultraviolet (UV) Radiation
The sun emits various types of UV radiation, categorized primarily as UVA and UVB. UVA radiation penetrates deeply into the skin, contributing to premature aging, wrinkles, and long-term damage. UVB radiation, while less penetrating, is primarily responsible for sunburn and plays a significant role in skin cancer development. Understanding the different types of UV radiation and their respective effects helps in choosing the appropriate protection measures.
Sun Protection Factor (SPF)
The Sun Protection Factor (SPF) is a numerical rating that indicates how effectively a sunscreen protects against UVB radiation. A higher SPF number signifies greater protection. SPF 15 blocks approximately 93% of UVB rays, while SPF 30 blocks about 97%, and SPF 50 blocks around 98%. It’s important to note that SPF only measures protection against UVB rays; separate measures are necessary for UVA protection.
SPF Levels and Suitable Activities
| SPF Level | Protection Level | Suitable Activities |
|---|---|---|
| 15 | Moderate protection | Everyday activities in moderate sun exposure, such as short trips to the park or errands. |
| 30 | High protection | Extended outdoor activities, like swimming, hiking, or spending time at the beach on a sunny day. |
| 50 | Very high protection | Activities involving prolonged sun exposure, such as outdoor sports, long beach trips, or extended periods in direct sunlight. |
Applying sunscreen with a high SPF, like 30 or 50, is highly recommended for extended outdoor activities. The selection of SPF level should be tailored to the intensity and duration of sun exposure.
Sun Protection Methods
Beyond the fundamentals of sun protection, employing various methods effectively amplifies your defense against harmful UV rays. Understanding the diverse approaches and their specific strengths is crucial for comprehensive sun safety. This section delves into practical strategies, from clothing choices to sunscreen selection, empowering you to build a robust sun protection plan.
Clothing
Appropriate clothing acts as a significant barrier against UV radiation. Fabric density and weave directly influence UV protection. Tightly woven, dark-colored fabrics generally offer better shielding than loose, light-colored ones. Look for clothing labeled with a UV protection factor (UPF) rating. A higher UPF number indicates greater protection. For instance, a UPF 50 rating blocks 98% of UVB radiation. Choosing long-sleeved shirts and long pants during peak sun hours provides further coverage.
Hats
Wide-brimmed hats effectively shade the face, ears, and neck, crucial areas vulnerable to sun damage. A wide brim, extending at least 4 inches around the head, offers substantial protection from the sun’s rays. Straw hats, baseball caps, and even floppy sun hats can provide varying levels of shade. The choice depends on personal preference and the specific activity.
Sunglasses
Protecting your eyes is vital for sun safety. High-quality sunglasses with UV protection filters block harmful UVA and UVB rays, safeguarding your eyes from long-term damage. Look for sunglasses with a label indicating 100% UV protection. These filters are crucial to preventing cataracts and macular degeneration, prevalent eye conditions associated with sun exposure.
Sunscreen
Sunscreen is a critical component of a comprehensive sun protection strategy. It forms a physical barrier on the skin, preventing UV radiation from penetrating. Applying sunscreen correctly and consistently is essential for optimal protection. Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with a sun protection factor (SPF) of 30 or higher. Reapplication is paramount, especially after swimming or sweating.
Sunscreen Selection Criteria
Selecting the right sunscreen involves careful consideration of various factors. A broad-spectrum sunscreen is essential, protecting against both UVA and UVB rays. Look for a high SPF (Sun Protection Factor) rating, such as 30 or higher. A higher SPF indicates greater protection. The consistency of the sunscreen is another consideration. Some people prefer lotions, gels, or sprays, depending on their personal preference and skin type.
Mineral vs. Chemical Sunscreens
Mineral sunscreens utilize mineral ingredients like zinc oxide and titanium dioxide to create a physical barrier, reflecting UV rays. Chemical sunscreens absorb UV rays and convert them into heat, which is then released. Both types provide effective protection when used correctly. The choice between mineral and chemical sunscreens often depends on individual preferences, such as potential skin reactions or environmental concerns.
Sun Protection Methods Comparison
| Method | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Clothing | Effective barrier, readily available, affordable | Can be uncomfortable in hot weather, may not cover all areas |
| Hats | Excellent protection for head, face, and neck, easy to use | May not provide complete coverage of other areas, can be cumbersome for certain activities |
| Sunglasses | Protects eyes from UV damage, readily available | Can be uncomfortable for some, may not be suitable for all activities |
| Sunscreen (Mineral) | Generally considered gentle on skin, environmentally friendly | May have a white cast on skin, can be slightly thicker |
| Sunscreen (Chemical) | Often less visible on skin, available in various textures | Potential for allergic reactions in some individuals, concerns about environmental impact |
Sunscreen Application and Usage
Proper sunscreen application is crucial for maximizing its protective effect. Applying sunscreen correctly and reapplying it regularly, especially during prolonged sun exposure, significantly reduces the risk of sunburn and long-term skin damage. This section details the correct application procedures, frequency, and considerations for different individuals.
Sunscreen Application Steps
Effective sunscreen application involves a meticulous process. A generous amount is essential to ensure adequate coverage of exposed skin. Applying sunscreen 15-30 minutes before sun exposure allows the product to absorb and form a protective barrier. Avoid areas where the sunscreen may rub off easily.
- Thoroughly cleanse and dry the skin area to be protected. This removes any dirt, oil, or makeup that could interfere with sunscreen absorption.
- Apply a sufficient amount of sunscreen. A general guideline is one ounce for the average adult’s body. This is equivalent to approximately a shot glass full.
- Evenly distribute the sunscreen across all exposed skin areas. This includes the face, neck, ears, hands, and feet. Use a circular motion for even coverage, avoiding streaks or clumps.
- Pay close attention to frequently missed areas like the tops of the feet, backs of the knees, and the hairline. Be especially thorough around the eyes and lips.
- Ensure complete coverage of the entire area to be protected. This includes areas like the back of the neck, ears, and the tops of the feet.
- Reapply sunscreen every two hours, or more frequently if swimming or sweating. This ensures continuous protection against the sun’s harmful UV rays.
Reapplication Frequency
The frequency of sunscreen reapplication is critical, especially during extended sun exposure. Frequent reapplication is necessary to maintain the protective effect of the sunscreen. The specific intervals for reapplication depend on the activity and environmental conditions. For example, activities like swimming or sweating may require more frequent reapplication to maintain the sunscreen’s protective barrier.
- Reapply sunscreen every two hours, or more frequently if swimming or sweating. This helps maintain the protective barrier and prevent sunburn.
- In situations of extended sun exposure, reapplication every hour or less may be necessary. This depends on the individual’s skin sensitivity, the intensity of the sun, and their activities.
- It’s essential to pay close attention to specific guidelines on the sunscreen product packaging. Different sunscreen products may have varying recommendations for reapplication.
Application Scenarios
Different scenarios require specific application considerations. Understanding these nuances is essential for effective sun protection. For instance, children’s skin is more sensitive, while athletes may need more frequent reapplication due to sweating and exposure.
| Scenario | Considerations |
|---|---|
| Children | Use a child-friendly sunscreen with a high SPF. Apply liberally and frequently, especially around sensitive areas like the face and hands. |
| Athletes | Choose a water-resistant sunscreen with a high SPF. Reapply frequently, especially after swimming or sweating. |
| Individuals with sensitive skin | Select a gentle, hypoallergenic sunscreen with a high SPF. Apply thinly and avoid areas that might be irritated. |
Step-by-Step Guide for Applying Sunscreen, Sun protection tips
This guide provides a systematic approach for applying sunscreen, ensuring thorough coverage and protection.
- Gather necessary items, including sunscreen, a clean towel, and a mirror.
- Prepare the application area by cleansing and drying the skin.
- Apply a generous amount of sunscreen, approximately one ounce for the average adult.
- Evenly distribute the sunscreen over all exposed skin using circular motions.
- Pay special attention to areas prone to sunburn, like the ears, nose, and back of the neck.
- Reapply sunscreen every two hours, or more often if engaging in activities that cause sweating or water exposure.
Sun Protection for Different Individuals
Sun protection is crucial for everyone, but the specific strategies need tailoring to individual needs. Different factors, like age, medical conditions, and lifestyle, affect how much UV radiation a person can tolerate. This section delves into sun protection strategies for various groups, highlighting the importance of prevention in skin cancer and the factors influencing individual sun sensitivity.
Understanding the diverse needs of different groups is vital for effective sun protection. Tailored strategies can significantly reduce the risk of skin damage and associated health concerns, promoting overall well-being.
Sun Protection for Children
Children’s skin is particularly vulnerable to sun damage due to its thinner nature and lower melanin content. Children’s skin is more sensitive to UV radiation than adults, making them more susceptible to sunburn and long-term skin damage. Prolonged exposure can increase the risk of skin cancer later in life.
- Utilize broad-spectrum sunscreens with an SPF of 30 or higher for children. Apply liberally and frequently, reapplying every two hours or after swimming or sweating.
- Seek shade whenever possible, especially during peak sun hours (10 am to 4 pm).
- Dress children in protective clothing, such as long-sleeved shirts, pants, and wide-brimmed hats.
- Educate children about sun safety habits, including the importance of seeking shade and using sunscreen.
Sun Protection for the Elderly
As individuals age, their skin often loses elasticity and protective capacity. The skin’s natural repair mechanisms may also be less efficient, increasing the risk of sunburn and skin damage. Age-related thinning of the skin can lead to greater susceptibility to skin cancer.
- Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher, applying liberally and reapplying frequently.
- Seek shade during peak sun hours.
- Wear protective clothing, including hats, sunglasses, and long-sleeved shirts.
- Regular skin checks are essential for early detection of skin changes, which can be indicators of skin cancer.
Sun Protection for Individuals with Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions can affect a person’s sensitivity to the sun. For example, individuals taking certain medications may experience increased photosensitivity, making them more susceptible to sunburn. Conditions like vitiligo or lupus can also impact skin’s ability to protect itself from the sun’s harmful rays.
- Consult a dermatologist or healthcare provider for personalized recommendations regarding sun protection based on specific medical conditions.
- Follow the advice of healthcare professionals regarding medication interactions and sun exposure.
- Be aware of potential increased sun sensitivity associated with specific medications.
- Individuals with conditions like lupus or vitiligo may require extra caution and proactive sun protection measures.
Factors Influencing Individual Sun Sensitivity
Skin type, genetics, and lifestyle all play a role in how sensitive a person is to the sun. Individuals with fair skin, light hair, and light eyes tend to be more susceptible to sunburn than those with darker complexions. Exposure to certain environmental factors, such as high altitude or pollution, can also influence sun sensitivity.
| Factor | Impact on Sun Sensitivity |
|---|---|
| Skin type (fair skin) | Increased susceptibility to sunburn and skin damage |
| Genetics | Predisposition to skin cancer can be inherited |
| Lifestyle (outdoor activities) | Increased cumulative sun exposure |
| Altitude | Higher altitude increases UV radiation |
Sun Protection and Skin Cancer Prevention
Prolonged and excessive sun exposure is a significant risk factor for skin cancer. Protecting the skin from the sun’s harmful UV rays is a crucial preventative measure. Early detection and treatment of skin cancer are critical for positive outcomes.
“Regular sun protection measures can substantially reduce the risk of skin cancer.”
Resources for Further Information
- The Skin Cancer Foundation: Provides valuable information on skin cancer prevention, early detection, and treatment options.
- The American Academy of Dermatology: Offers expert advice on skin health, including sun protection guidelines and recommendations.
- National Cancer Institute: Provides comprehensive information on skin cancer, including statistics, research, and treatment options.
Sun Protection in Different Environments
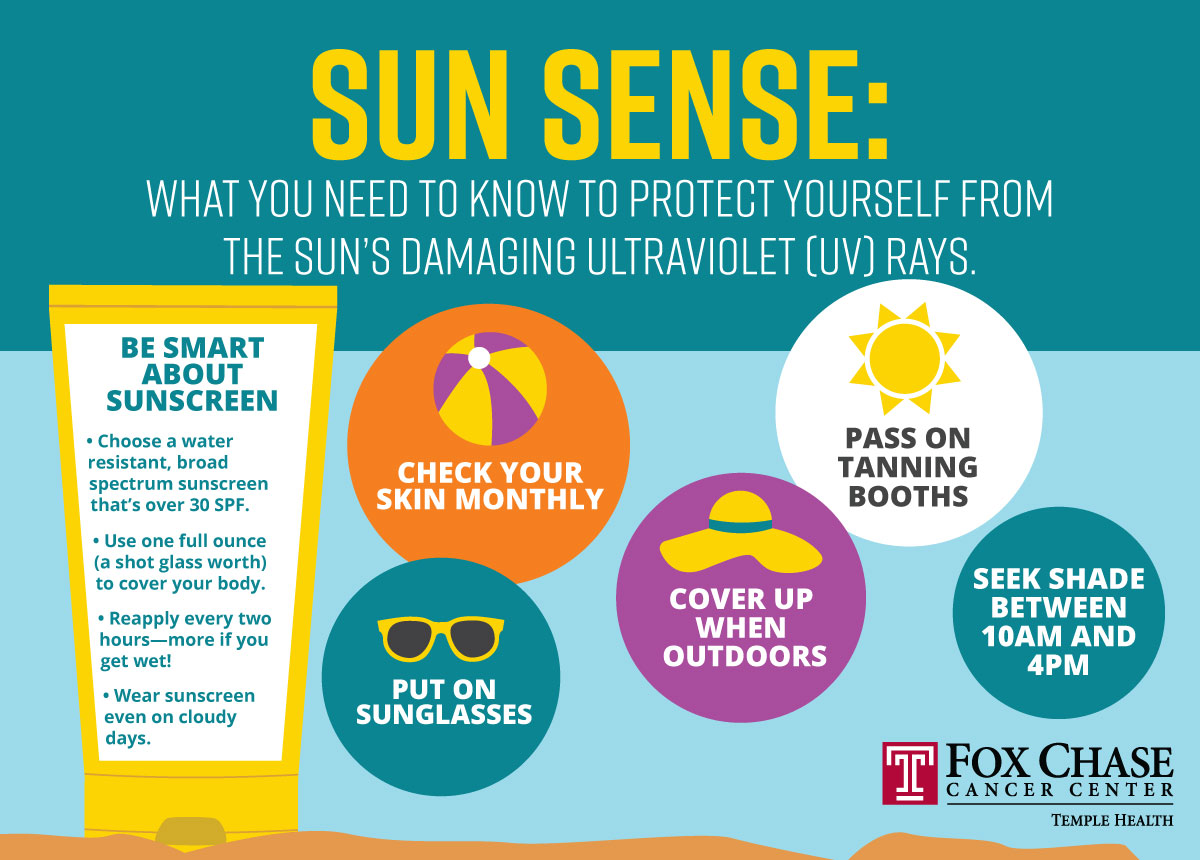
Understanding sun protection needs is crucial for effective sun safety. Factors like geographical location, time of year, and the type of outdoor activity significantly influence the level of sun protection required. This section explores how to adapt sun protection strategies for diverse environments and activities.
Geographic location and seasonal variations play a significant role in determining sun exposure. Higher altitudes and proximity to the equator typically experience stronger and more intense ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Furthermore, the angle of the sun throughout the year directly affects the amount of UV radiation reaching the Earth’s surface. This variation necessitates adjusting sun protection measures accordingly.
Sun Protection Needs by Geographic Location
Different geographical locations have unique sun exposure patterns. Coastal areas, especially beaches, experience high UV radiation levels, demanding consistent and diligent sun protection measures. Mountainous regions, though often perceived as cooler, can experience significant UV radiation at high altitudes. Deserts, with their clear skies and minimal cloud cover, receive intense UV radiation, requiring maximum sun protection. These differing levels of sun exposure necessitate tailored strategies.
Sun Protection During Outdoor Activities
Outdoor activities significantly impact sun exposure. Water activities like swimming and boating expose individuals to reflected UV radiation from the water’s surface, increasing their sun exposure risk. Hiking, especially at high altitudes, necessitates robust sun protection due to the thinner atmosphere and increased UV radiation. Outdoor sports, such as tennis and golf, demand consistent protection throughout the duration of the activity. These considerations are crucial for effective sun protection.
Sun Protection Strategies for Different Climates
Various climates necessitate specific sun protection strategies. Deserts require high-SPF sunscreens and frequent reapplication, considering the intense UV radiation. Beachgoers should employ UV-protective clothing, hats, and sunglasses, alongside high-SPF sunscreens, due to the reflected UV radiation from the water’s surface. Mountain climbers should use high-SPF sunscreens, wear protective clothing, and consider UV-blocking eyewear to mitigate the increased UV exposure at higher altitudes. Choosing the appropriate protective measures for each climate is essential.
Adapting Sun Protection for Different Activities
Different outdoor activities demand tailored sun protection measures. Hikers benefit from long-sleeved shirts, pants, and hats, along with high-SPF sunscreen, especially during prolonged periods of exposure. Swimmers should reapply sunscreen frequently, due to water’s reflective properties. Outdoor workers, particularly those exposed to the sun for extended periods, should utilize protective clothing, sunglasses, and hats, in addition to high-SPF sunscreen. These activities necessitate adaptable sun protection measures.
Sun Protection and Daily Habits
Integrating sun protection into your daily routine is crucial for long-term skin health. Consistent practices, combined with awareness of your individual needs, significantly reduce your risk of premature aging and skin damage. This proactive approach is more effective than reacting to sunburns.
A well-structured sun protection plan extends beyond just applying sunscreen. It encompasses a comprehensive understanding of how sun exposure interacts with your body, including its impact on vitamin D production, hydration, and overall daily activities.
Importance of Incorporating Sun Protection into Daily Routines
Consistent sun protection is vital for maintaining healthy skin and reducing the risk of skin cancer and premature aging. By integrating protective measures into your daily routine, you establish a sustainable approach to sun safety. This consistency is far more effective than sporadic application of sunscreen or other protective measures.
Relationship Between Sun Exposure and Vitamin D Production
The relationship between sun exposure and vitamin D production is complex. While sunlight is essential for vitamin D synthesis, excessive exposure can lead to skin damage. A balanced approach is necessary. Limited, controlled exposure can contribute to vitamin D levels, while prolonged or unprotected exposure can lead to skin issues.
Role of Hydration in Maintaining Healthy Skin During Sun Exposure
Proper hydration plays a critical role in maintaining healthy skin, especially during sun exposure. Adequate water intake helps to keep skin cells hydrated, improving skin elasticity and reducing the risk of dryness and damage from sun exposure. Dehydrated skin is more susceptible to sun damage.
Tips for Incorporating Sun Protection into Everyday Activities
Maintaining sun protection throughout the day requires strategic planning and mindful choices. Here are some practical tips to integrate sun protection into everyday activities:
- Schedule Outdoor Activities: Plan outdoor activities for the cooler parts of the day, such as early mornings or late evenings, to minimize direct sun exposure during peak hours. For example, scheduling a walk in the park for 6 am or 7 pm, rather than noon.
- Dress Appropriately: Wear protective clothing, such as long sleeves, pants, and wide-brimmed hats, when outdoors. This provides a physical barrier against the sun’s rays. A simple example is wearing a baseball cap when walking the dog during the hottest part of the day.
- Seek Shade: Whenever possible, seek shade under trees, umbrellas, or other structures to limit direct sun exposure. For example, taking a break under a tree while walking or sitting in a shaded area during a picnic.
- Apply Sunscreen Regularly: Apply broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher to exposed skin, at least 15-30 minutes before sun exposure. Reapply every two hours, or more frequently if swimming or sweating. This consistent application is crucial for maintaining sun protection throughout the day.
- Use Sunglasses: Protect your eyes with sunglasses that block both UVA and UVB rays. This simple measure protects the delicate skin around the eyes from sun damage.
- Monitor UV Index: Check the UV index forecast before heading outdoors. Higher UV index values indicate increased risk of sun damage and necessitate more rigorous sun protection measures. Understanding the UV index is critical for planning outdoor activities.
- Hydrate Effectively: Drink plenty of water throughout the day, especially during outdoor activities. Dehydration can exacerbate the effects of sun exposure on the skin. Carrying a water bottle and taking sips throughout the day is a practical solution.
Sun Protection for Specific Skin Concerns

Protecting your skin from the sun is crucial for overall well-being, and this is especially true for individuals with specific skin conditions. Understanding how sun exposure impacts different skin types and tones, and tailoring sun protection strategies accordingly, is essential for maintaining healthy skin. This section delves into sun protection strategies for various skin conditions, highlighting the risks associated with different skin tones and emphasizing the importance of sun protection for general skin health.
Sun Protection for Acne-Prone Skin
Acne-prone skin often exhibits sensitivity to harsh ingredients and products. Sunscreens with non-comedogenic formulations, meaning they are less likely to clog pores, are crucial. Look for water-based or gel-based formulas, which are typically lighter and less likely to exacerbate breakouts. Avoid oil-based sunscreens, as these can increase oil production and potentially worsen acne.
Sun Protection for Sensitive Skin
Sensitive skin reacts easily to various environmental factors, including UV radiation. Opt for broad-spectrum sunscreens specifically designed for sensitive skin. These formulations often contain hypoallergenic and gentle ingredients. Test any new sunscreen on a small area of skin before applying it to the entire body to identify any allergic reactions. Look for fragrance-free and alcohol-free options.
Sun Protection for Different Skin Tones
Different skin tones have varying levels of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color. Melanin acts as a natural sunscreen, protecting against UV radiation. Individuals with lighter skin tones are generally more susceptible to sunburn and skin damage from sun exposure, requiring higher levels of sun protection. Individuals with darker skin tones are not immune to sun damage, but their risk is often lower due to melanin’s protective effect. While darker skin tones may experience less visible signs of sun damage, long-term sun exposure can still lead to skin aging, hyperpigmentation, and other issues.
Sun Protection Product Comparison
| Skin Type | Sunscreen Recommendation | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Acne-Prone | Water-based, gel-based, non-comedogenic | Lightweight, less likely to clog pores, avoids oil-based formulations. |
| Sensitive Skin | Broad-spectrum, hypoallergenic, fragrance-free, alcohol-free | Gentle formulations, minimizes potential allergic reactions. |
| Light Skin Tone | High SPF, broad-spectrum | Provides maximum protection against UV radiation. |
| Darker Skin Tone | Broad-spectrum, moderate SPF | Balances protection with minimal irritation. |
Consistent sun protection, regardless of skin tone, is essential for preventing premature aging and skin cancer.
Benefits of Sun Protection for Overall Skin Health
Sun protection extends beyond immediate concerns, contributing to long-term skin health. Consistent use of sun protection products minimizes the risk of sunburn, premature aging, wrinkles, and hyperpigmentation. Protecting the skin from harmful UV rays also significantly reduces the risk of skin cancer, a serious health concern.
Final Thoughts: Sun Protection Tips
In conclusion, consistent sun protection is vital for overall skin health and reducing the risk of skin cancer. By understanding the basics of sun protection, choosing the right methods, and incorporating these practices into your daily routine, you can significantly minimize your exposure to harmful UV rays. Remember, sun protection is an ongoing commitment, and consistent effort will pay off in the long run.
Protecting your skin from the sun is key, obviously. Using a broad-spectrum sunscreen with a high SPF is a must. And incorporating ingredients like squalane for skin squalane for skin can enhance your skin’s natural moisture barrier, making it more resilient to sun damage. So, remember to layer up your sun protection routine for optimal results.
Protecting your skin from the sun is crucial, obviously. But did you know getting enough quality sleep is equally important for healthy skin? Proper sleep can significantly improve your skin’s resilience, leading to a more youthful appearance. Checking out beauty sleep tips can give you some valuable insights into that. Ultimately, combining these two aspects – sun protection and good sleep – will significantly contribute to your overall skin health.